Gut Health
February 8, 2026
TLDR: Yoga for Gut Health – The Science-Backed Poses That Talk to Your Nervous System
This article explores how yoga directly modulates the gut-brain axis to reduce gastrointestinal symptoms. Key points include:
The 2025 systematic review findings on yoga for IBS (PMID: 41108584)
How the vagus nerve connects stress to digestive dysfunction
Specific poses matched to specific GI symptoms
The critical role of breathwork alongside physical postures
Key takeaways:
Yoga reduced IBS symptom severity with moderate-to-large effect sizes across 10 clinical studies
In one trial, yoga performed as well as a low-FODMAP diet for symptom management
70-90% of gut-brain signals travel upward—meaning your gut is constantly informing your brain
The strongest results came from programs combining postures + breathwork + meditation, not just stretching
Consistency beats intensity: 2-3 sessions per week for 6-12 weeks shows measurable change
Wise Mind Nutrition's stance:
Supports yoga as an evidence-based intervention for functional GI disorders
Emphasizes the gut-brain axis as a key therapeutic target often overlooked in conventional care
Encourages matching specific poses to specific symptoms rather than generic "yoga for digestion" advice
Promotes breathwork as an accessible, no-cost tool for vagus nerve stimulation
Views yoga as complementary to nutritional interventions like the low-FODMAP diet, not a replacement
The article concludes that your gut doesn't need more willpower—it needs a different signal from your nervous system. Yoga is one of the few interventions that addresses both the physical and neurological drivers of GI dysfunction simultaneously. Start with 3 poses that match your symptoms, add 5 minutes of breathwork, and commit to 6 weeks.
[Read full article for pose-by-pose instructions, breathwork techniques, dosing recommendations from clinical trials, and full references to peer-reviewed research]

Your gut contains 500 million neurons. It doesn't just digest food—it thinks, reacts, and remembers stress. This is not a metaphor. The enteric nervous system, often called the second brain, operates with remarkable autonomy while maintaining constant communication with your central nervous system through the vagus nerve [1].
For the millions of people suffering from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), functional dyspepsia, or stress-driven digestive symptoms, this gut-brain connection isn't abstract science—it's lived experience. You feel anxiety in your stomach. You know that stress changes your digestion. What you may not know is that yoga can talk back to this system—directly.
What the Research Actually Shows

A 2025 systematic review published in Comprehensive Physiology analyzed 10 clinical studies examining yoga interventions for IBS [2]. The findings were striking: yoga reduced gastrointestinal symptom severity with moderate-to-large effect sizes (Cohen's d range: 0.37–3.60). In one head-to-head trial, yoga performed as well as a low-FODMAP diet—one of the most commonly prescribed dietary interventions for IBS.
This isn't isolated. A previous systematic review in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology found evidence of yoga's beneficial effects compared with conventional treatment, with significantly reduced bowel symptoms, IBS severity, and anxiety [3]. Another systematic review examining exercise therapies for IBS specifically highlighted yoga as showing significant benefits for gastrointestinal symptoms [4].
Why Yoga Works: The Gut-Brain Axis Mechanism
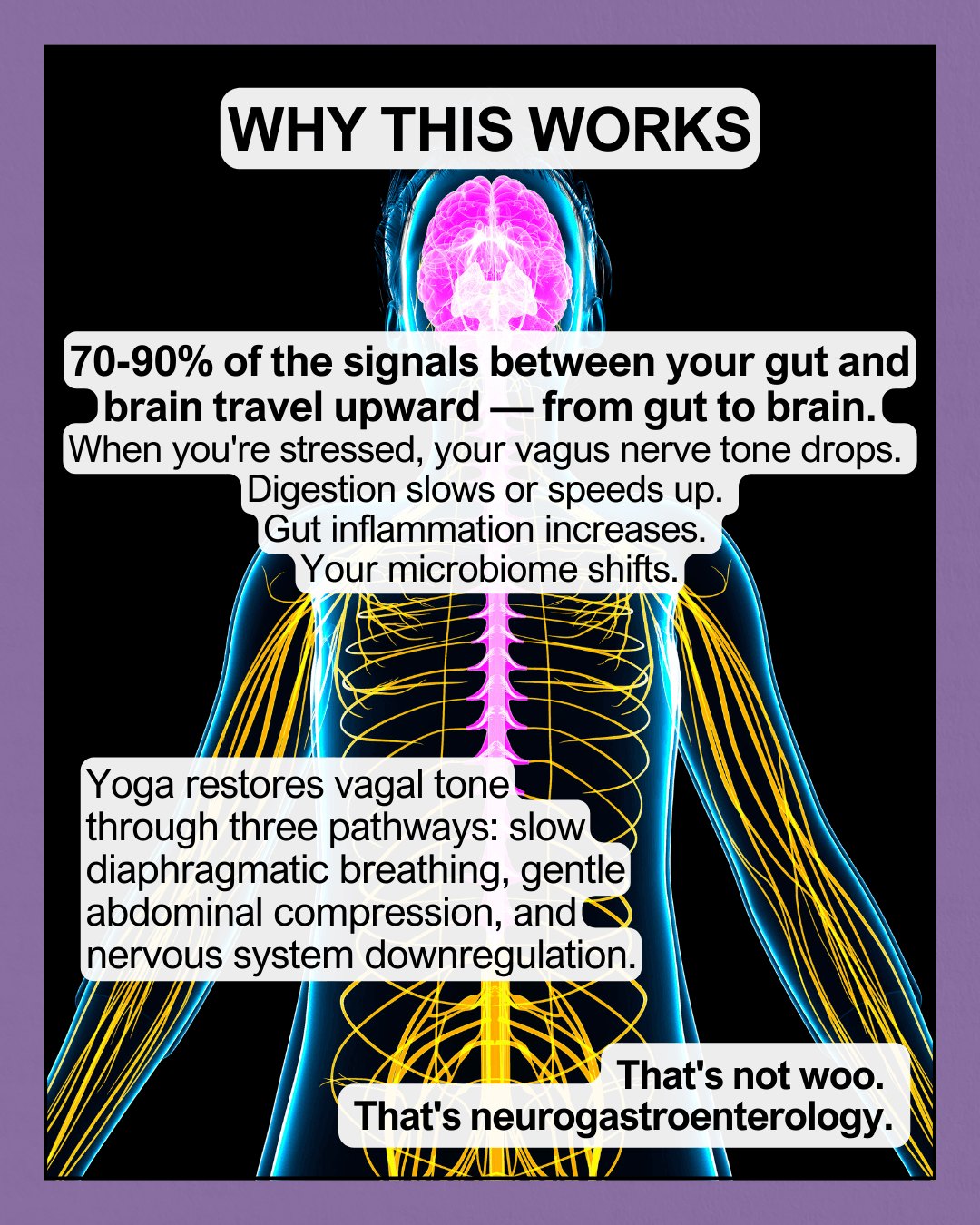
Here's what most people miss: yoga doesn't just "relax" you. It directly modulates your gut-brain axis through the vagus nerve—the superhighway between your brain and your digestive tract.
Approximately 70-90% of the signals between your gut and brain travel upward—from gut to brain [1,5]. When you're stressed, your vagus nerve tone drops. Digestion slows or speeds up erratically. Gut inflammation increases. Your microbiome shifts toward less favorable bacterial populations.
Yoga restores vagal tone through three pathways: slow diaphragmatic breathing, gentle abdominal compression, and nervous system downregulation. The strongest results in clinical trials came from programs that combined postures, breathwork, and a meditative component—not just stretching [2].
That's not woo. That's neurogastroenterology.
Poses for Bloating & Gas

These poses create gentle compression and release in the abdomen, helping trapped gas move through the digestive tract.
Pavanamuktasana (Wind-Relieving Pose): Lie on your back, hug one knee to your chest, hold 30–60 seconds, then switch sides. The name literally translates to "wind-relieving pose"—traditional yogis knew what they were doing.
Ananda Balasana (Happy Baby Pose): Grab the outsides of your feet, knees wide, with a gentle rock side to side. This opens the lower abdomen and can help release abdominal tension.
Poses for Constipation
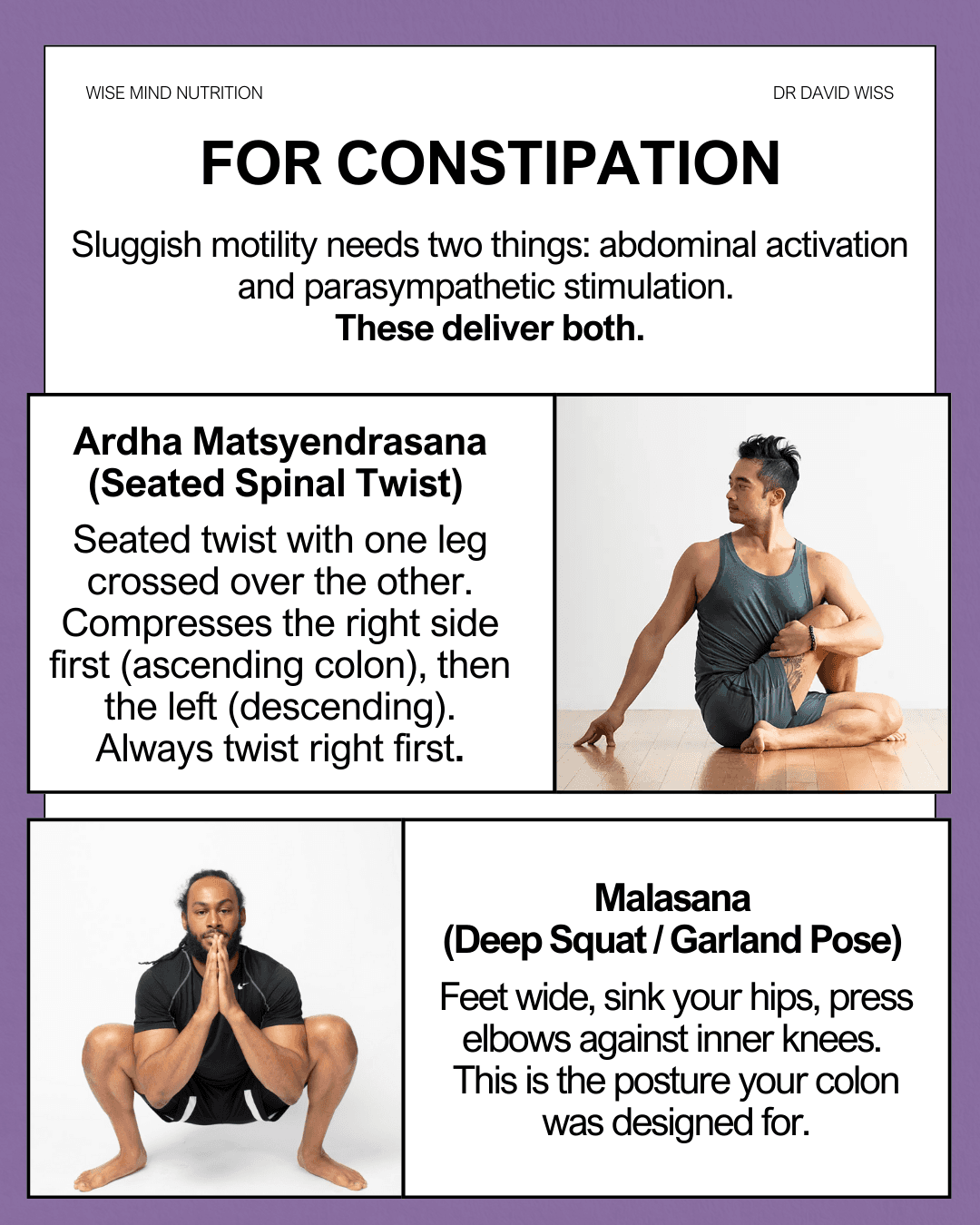
Sluggish motility needs two things: abdominal activation and parasympathetic stimulation. These poses deliver both.
Ardha Matsyendrasana (Seated Spinal Twist): A seated twist with one leg crossed over the other. Compresses the right side first (ascending colon), then the left (descending colon). Always twist right first to follow the direction of digestive flow.
Malasana (Deep Squat/Garland Pose): Feet wide, sink your hips, press elbows against inner knees. This is the posture your colon was designed for—the squatting position optimizes the anorectal angle for elimination.
Poses for IBS with Diarrhea / Urgency
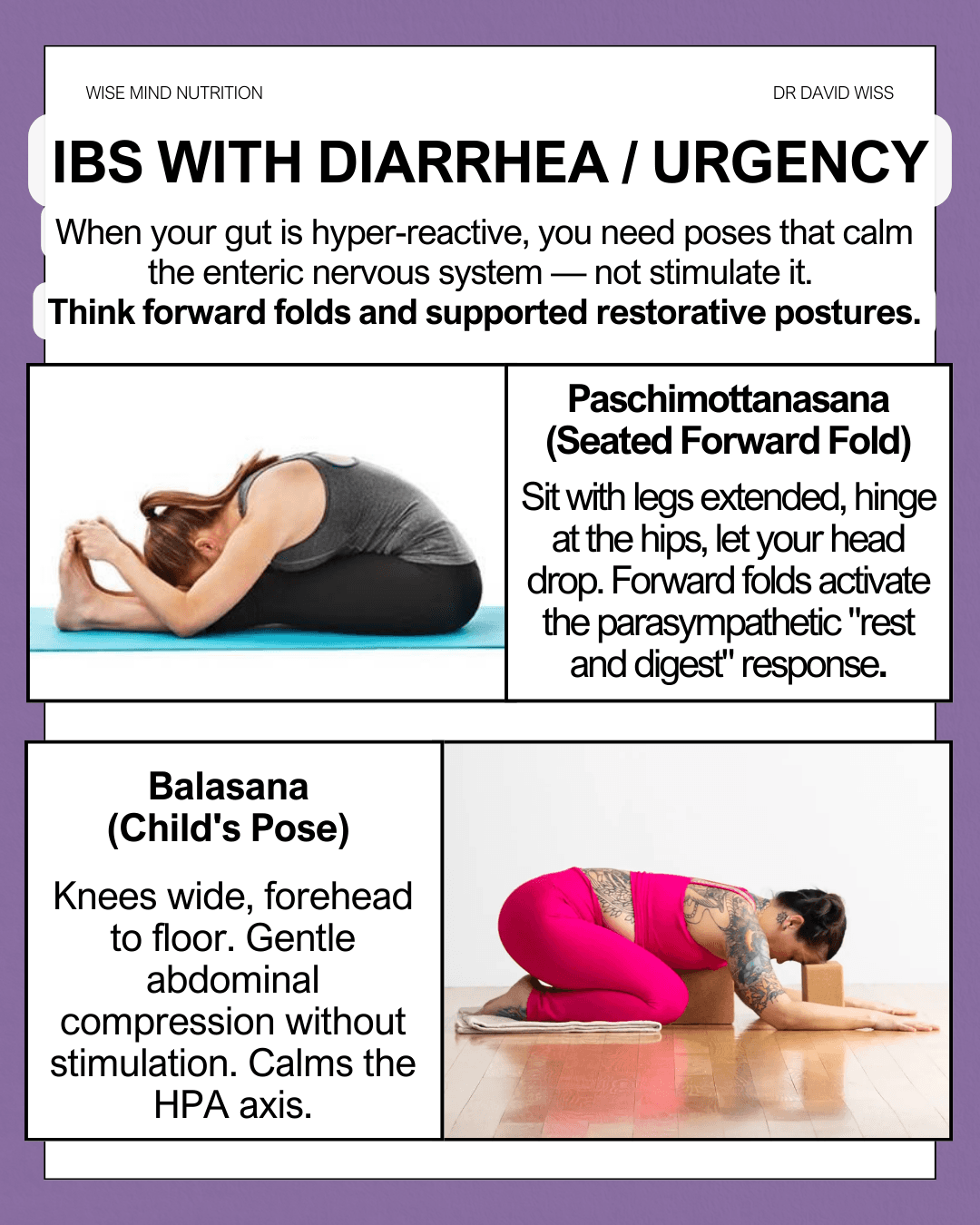
When your gut is hyper-reactive, you need poses that calm the enteric nervous system—not stimulate it. Think forward folds and supported restorative postures.
Paschimottanasana (Seated Forward Fold): Sit with legs extended, hinge at the hips, let your head drop. Forward folds activate the parasympathetic "rest and digest" response and can help reduce visceral hypersensitivity—a key driver of IBS-D symptoms.
Balasana (Child's Pose): Knees wide, forehead to floor. Provides gentle abdominal compression without stimulation. This pose directly calms the HPA (hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal) axis, reducing the stress hormones that can accelerate gut transit.
Poses for Stress-Driven GI Symptoms

For GERD, nervous stomach, and functional dyspepsia—conditions where stress is often the upstream driver—your priority is activating the vagus nerve.
Viparita Karani (Legs Up the Wall): Lie on your back, legs extended up a wall, arms relaxed. Hold for 5–10 minutes. This is one of the fastest ways to shift from sympathetic (fight-or-flight) to parasympathetic (rest-and-digest) dominance.
Setu Bandhasana (Supported Bridge Pose): Place a block or bolster under your sacrum. This gentle inversion calms the nervous system and opens the diaphragm—helpful for GERD-type symptoms when used well after meals (not immediately after eating).
The Breathwork Component: Don't Skip This
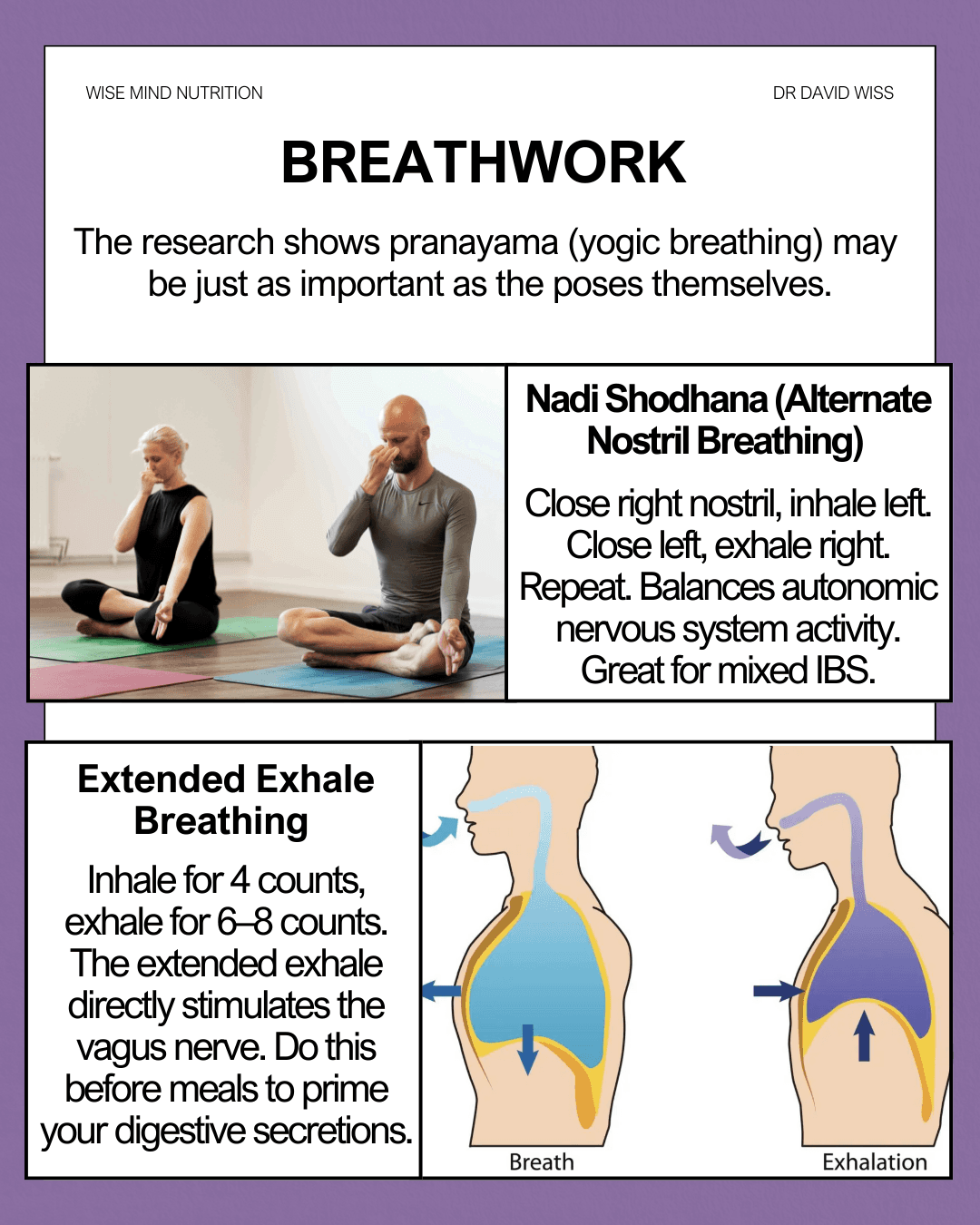
The research suggests that pranayama (yogic breathing) may be just as important as the poses themselves [2]. The breathing component is what separates yoga from simple stretching exercises—and likely explains its superior effects on gut-brain axis disorders.
Nadi Shodhana (Alternate Nostril Breathing): Close right nostril, inhale left. Close left, exhale right. Repeat. This balances autonomic nervous system activity and is particularly useful for mixed IBS presentations.
Extended Exhale Breathing: Inhale for 4 counts, exhale for 6–8 counts. The extended exhale directly stimulates the vagus nerve. Try doing this before meals to prime your digestive secretions.
These techniques are free, require no mat, and can be done anywhere—including in a bathroom stall before a stressful meeting.
How Much Yoga Do You Actually Need?

Based on the clinical trial data [2]:
Frequency: 2–3 sessions per week (minimum)
Duration: 6–12 weeks to see measurable change
Session length: 30–60 minutes
Home practice: Even 10–15 minutes daily adds up
Importantly, higher adherence was directly linked to greater symptom improvement across multiple studies. Consistency beats intensity here.
The Bottom Line

Your gut doesn't need more willpower. It needs a different signal from your nervous system.
Yoga is one of the few interventions that addresses both the physical and neurological drivers of GI dysfunction simultaneously. The research supports its use as a feasible, safe, and effective adjunctive treatment for functional gastrointestinal disorders [2,3,4].
Start with 3 poses from this article that match your symptoms. Add 5 minutes of breathwork. Commit to 6 weeks.
Your gut-brain axis will thank you.
References
[1] Kwiecien S, et al. Role of brain-gut axis in mechanism of gastrointestinal defense. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2025;76(5):487-499. PMID: 41364165. DOI: 10.26402/jpp.2025.5.01
[2] Pavan F, et al. The Effectiveness of Yoga for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Comprehensive Physiology. 2025;15:e70061. PMID: 41108584. DOI: 10.1002/cph4.70061
[3] Schumann D, et al. Effect of Yoga in the Therapy of Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(12):1720-1731. PMID: 27112106. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.04.026
[4] Zhou C, et al. Exercise therapy of patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018;31(2):e13461. PMID: 30232834. DOI: 10.1111/nmo.13461
[5] D'Silva A, et al. Meditation and Yoga for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2023;118(2):329-337. PMID: 36422517. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002052


